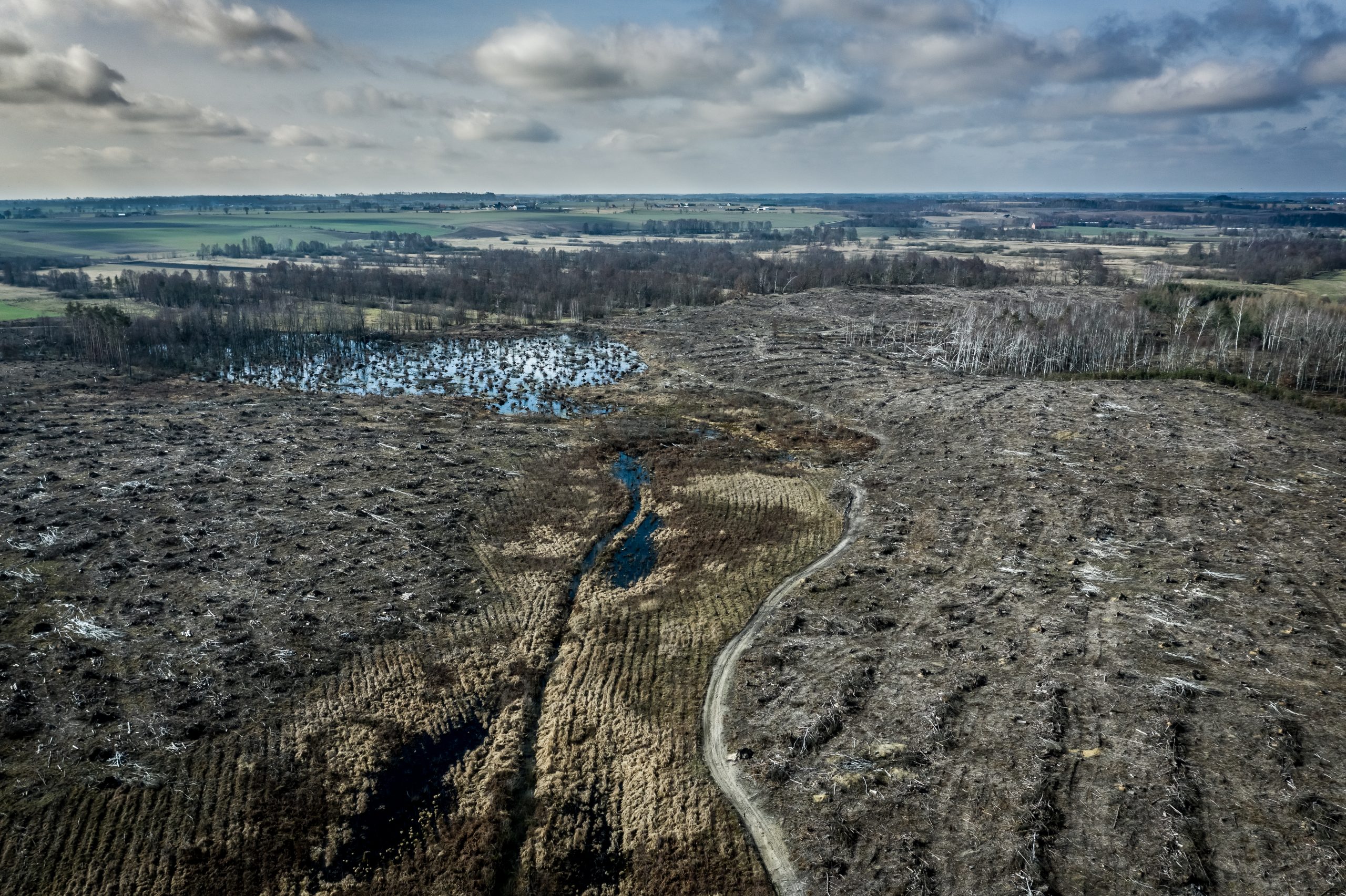
Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, is essential for the health and stability of our ecosystems. It includes the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems, all of which contribute to the balance and resilience of the natural world. However, biodiversity is currently facing an unprecedented crisis, with species extinction rates accelerating at an alarming pace. This article delves into the causes, impacts, and potential solutions to biodiversity loss, highlighting the urgency of addressing this critical issue.
Biodiversity loss refers to the decline in the number, variety, and variability of living organisms within a given ecosystem. This decline can occur at multiple levels, including the loss of species, genetic diversity within species, and ecosystem diversity. Biodiversity loss undermines the resilience of ecosystems, making them more vulnerable to environmental changes and human activities.
Habitat destruction is the leading cause of biodiversity loss. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion destroy the natural habitats of countless species, leaving them without food, shelter, or breeding grounds. The fragmentation of habitats also isolates populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of extinction.
Climate change significantly impacts biodiversity by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting the distribution and behavior of species. Some species may not be able to adapt quickly enough to changing conditions, leading to declines in populations and, ultimately, extinction.
Pollution, including air, water, and soil contamination, poses a severe threat to biodiversity. Chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants can poison wildlife, disrupt reproductive systems, and degrade habitats. Aquatic ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and plastic debris.
Overexploitation of natural resources, such as overfishing, hunting, and logging, directly reduces the populations of targeted species. Unsustainable practices can lead to the depletion of species and disrupt the balance of ecosystems, affecting other species that rely on them.
Invasive species, introduced intentionally or accidentally by human activities, can outcompete, prey on, or bring diseases to native species. These invasions can cause significant declines in native biodiversity and disrupt ecosystem functions.
Biodiversity underpins the ecosystem services that support human life, including pollination, water purification, soil fertility, and climate regulation. The loss of biodiversity can compromise these services, affecting food security, water quality, and overall human well-being.
The decline in biodiversity can have substantial economic impacts, particularly in sectors that rely on natural resources, such as agriculture, fisheries, and tourism. The loss of pollinators, for example, can reduce crop yields, while the decline in fish populations can impact livelihoods and food supply.
Biodiversity loss can increase health risks by reducing the availability of medicinal resources and increasing the prevalence of diseases. Many pharmaceutical products are derived from natural compounds found in diverse ecosystems. Additionally, the disruption of ecosystems can create conditions for the spread of infectious diseases.
Establishing and effectively managing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves, can safeguard critical habitats and provide safe havens for endangered species. Protected areas can also serve as research and education centers, raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
Adopting sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries can reduce the impact on biodiversity. This includes promoting organic farming, responsible fishing, and sustainable logging practices that maintain ecosystem health and productivity.
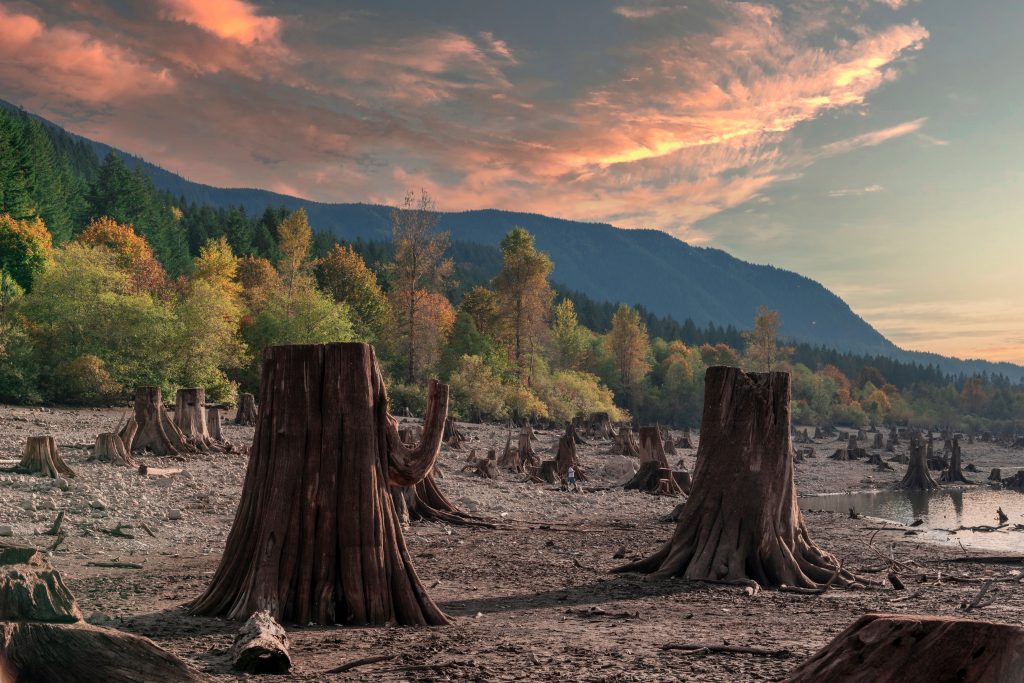

Ecological restoration projects aim to rehabilitate degraded ecosystems and reintroduce native species. Reforestation, wetland restoration, and the creation of wildlife corridors can enhance biodiversity and restore ecological balance.
Addressing climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the adoption of renewable energy sources is crucial for protecting biodiversity. Mitigation and adaptation strategies can help species and ecosystems cope with changing conditions.
Raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and advocating for conservation policies can drive collective action. Education programs, community engagement, and support for environmental organizations can empower individuals and communities to contribute to biodiversity conservation.
Biodiversity loss is a pressing global issue that demands immediate attention and action. The preservation of biodiversity is not only essential for the health of our planet but also for the well-being of human societies. By understanding the causes and impacts of biodiversity loss and implementing effective solutions, we can work towards a future where nature and humanity coexist harmoniously. Let us all take responsibility for protecting the incredible diversity of life on Earth, ensuring a resilient and sustainable world for generations to come.